A trainee once disagreed with him and when Dr. Sigerist asked him to estimate his authority, the student screamed, "You yourself said so!" "When?" asked Dr. Sigerist. "Three years back," responded to the trainee. "Ah," stated Dr. Sigerist, "3 years is a long period of time. I have actually changed my mind given that then." I guess for me this speaks with the changing tides of opinion which whatever remains in flux and open to renegotiation.
Much of this talk was paraphrased/annotated directly from the sources listed below, in specific the work of Paul Starr: Bauman, Harold, "Verging on National Health Insurance Coverage considering that 1910" in Altering to National Healthcare: Ethical and Policy Issues (Vol. 4, Principles in a Changing World) modified by Heufner, Robert P. and Margaret # P.
" Boost President's Plan", Washington Post, p. A23, February 7, 1992. Brown, Ted. "Isaac Max Rubinow", (a biographical sketch), American Journal of Public Health, Vol. 87, No. 11, pp. 1863-1864, 1997 Danielson, David A., and Arthur Mazer. "The Massachusetts Referendum for a National Health Program", Journal of Learn more Public Health Policy, Summer Season 1986.
" Your Home of Falk: The Paranoid Design in American House Politics", American Journal of Public Health", Vol. 87, No. 11, pp. 1836 1843, 1997. Falk, I (how did the patient protection and affordable care act increase access to health insurance?).S. "Propositions for National Medical Insurance in the U.S.A.: Origins and Evolution and Some Point Of Views for the Future', Milbank Memorial Fund Quarterly, Health and Society, pp.
Gordon, Colin. "Why No National Health Insurance Coverage in the United States? The Limitations of Social Provision in War and Peace, 1941-1948", Journal of Policy History, Vol. 9, No (a health care professional is caring for a patient who is taking zolpidem). 3, pp. 277-310, 1997. "History in a Tea Wagon", Time Publication, No. 5, pp. 51-53, January 30, 1939. Marmor, Ted. "The History of Healthcare Reform", Roll Call, pp.
Navarro, Vicente. "Medical History as a Justification Instead Of Explanation: Review of Starr's The Social Improvement of American Medication" International Journal of Health Services, Vol. 14, No. 4, pp. 511-528, 1984. Navarro, Vicente. "Why Some Nations Have National Health Insurance, Others Have National Health Service, and the United States has Neither", International Journal of Health Providers, Vol.
Fascination About Why Did Democrats Block Veterans Health Care Bill
3, pp. 383-404, 1989. Rothman, David J. "A Century of Failure: Healthcare Reform in America", Journal of Health Politics, Policy and Law", Vol. 18, No. 2, Summer 1993. Rubinow, Isaac Max. "Labor Insurance", American Journal of Public Health, Vol. 87, No. 11, pp. 1862 1863, 1997 (Initially released in Journal of Political Economy, Vol.
362-281, 1904). Starr, Paul. The Social Change of American Medicine: The rise of a sovereign profession and the making of a vast industry. Basic Books, 1982. Starr, Paul. "Transformation in Defeat: The Changing Objectives of National Health Insurance Coverage, 1915-1980", American Journal of Public Health, Vol. 72, No. 1, pp. 78-88, 1982 - why is health care so expensive.
" Crisis and Modification in America's Health System", American Journal of Public Health, Vol. 63, No. 4, April 1973. "Towards a https://writeablog.net/delodo1fzo/prevention-of-illness-and-promotion-of-health-and-wellbeing-international National Medical Care System: II. The Historic Background", Editorial, Journal of Public Health Policy, Autumn 1986. Trafford, Abigail, and Christine Russel, "Opening Night for Clinton's Plan", Washington Post Health Magazine, pp.
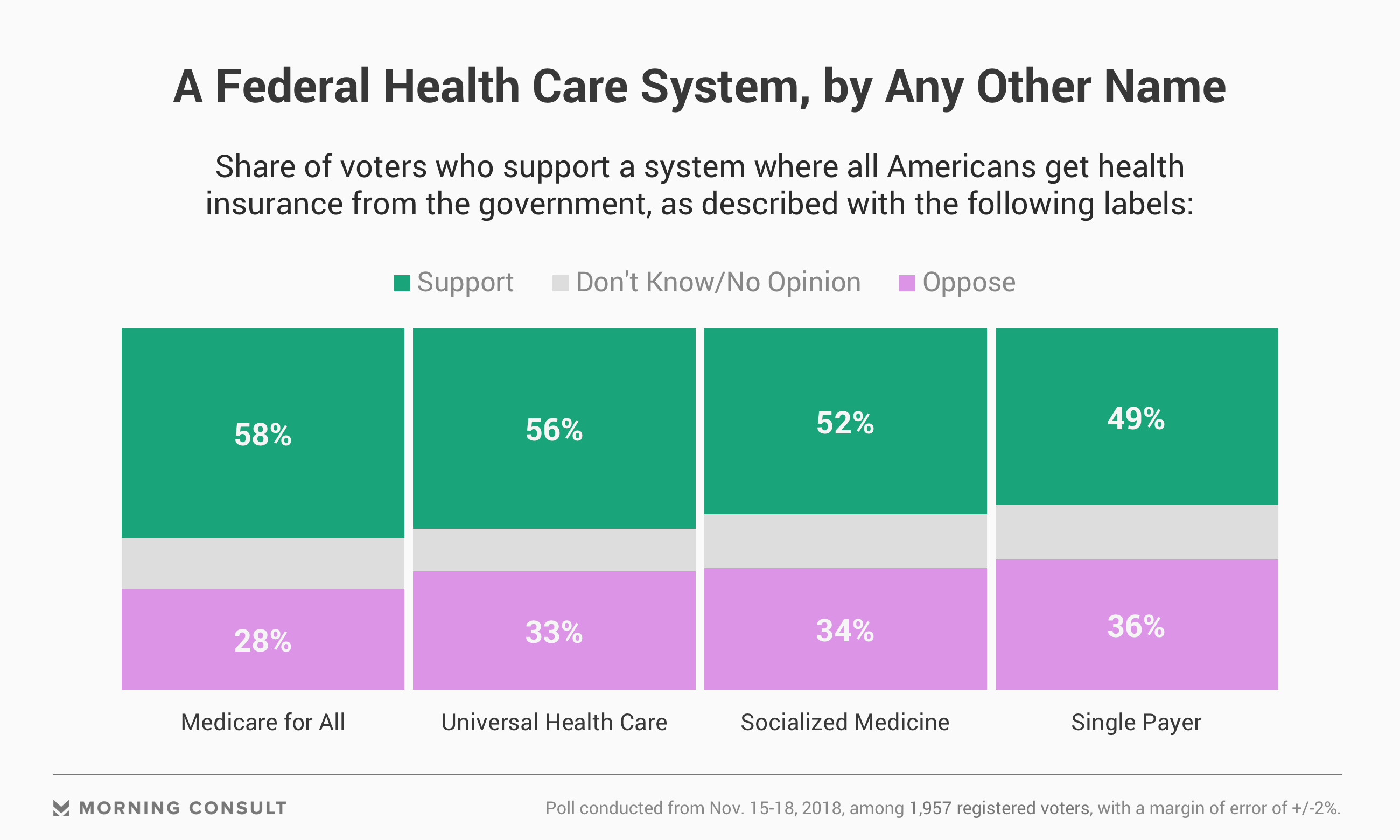
The United States does not have universal health insurance coverage. Almost 92 percent of the population was approximated to have protection in 2018, leaving 27.5 million people, or 8.5 percent of the population, uninsured. 1 Motion towards securing the right to healthcare has actually been incremental. 2 Employer-sponsored medical insurance was introduced throughout the 1920s.
In 2018, about 55 percent of the population was covered under employer-sponsored insurance coverage. 3 In 1965, the very first public insurance programs, Medicare and Medicaid, were enacted through the Social Security Act, and others followed. Medicare. Medicare guarantees a universal right to health care for persons age 65 and older. Qualified populations and the variety of benefits covered have actually slowly expanded.
All beneficiaries are entitled to traditional Medicare, a fee-for-service program that provides hospital insurance (Part A) and medical insurance coverage (Part B). Because 1973, recipients have actually had the choice to receive their coverage through either standard Medicare or Medicare Advantage (Part C), under which individuals register in a private health care organization (HMO) or managed care organization (how does universal health care work).
3 Simple Techniques For What Is Preventive Health Care
Medicaid. The Medicaid program initially provided states the option to get federal matching funding for supplying healthcare services to low-income households, the blind, and individuals with disabilities. Coverage was gradually made mandatory for low-income pregnant women and babies, and later for children approximately age 18. Today, Medicaid covers 17.9 percent of Americans.
Individuals need to make an application for Medicaid coverage and to re-enroll and recertify yearly. As of 2019, more than two-thirds of Medicaid recipients were registered in handled care organizations. 4 Kid's Medical insurance Program. In 1997, the Kid's Medical insurance Program, or CHIP, was created as a public, state-administered program for children in low-income households that make excessive to certify for Medicaid but that are unlikely to be able to afford personal insurance coverage.
5 In some states, it runs as an extension of Medicaid; in other states, it is a separate program. Inexpensive Care Act. In 2010, the passage of the Client Protection and Affordable Care Act, or ACA, represented the biggest growth to date of the federal government's role in financing and managing healthcare.
The ACA led to an estimated 20 million gaining coverage, decreasing the share of uninsured grownups aged 19 to 64 from 20 percent in 2010 to 12 percent in 2018.6 The federal government's responsibilities consist of: setting legislation and national strategies administering and spending for the Medicare program cofunding and setting basic requirements and regulations for the Medicaid program cofunding CHIP funding health insurance coverage for federal staff members along with active and previous members of the military and their families controling pharmaceutical items and medical gadgets running federal marketplaces for private health insurance providing premium aids for private marketplace protection.
The ACA established "shared responsibility" amongst federal government, companies, and people for ensuring that all Americans have access to cost effective and good-quality health insurance coverage. The U.S. Department of Health and Person Solutions is the Homepage federal government's primary agency involved with healthcare services. The states cofund and administer their CHIP and Medicaid programs according to federal regulations.
They likewise assist finance medical insurance for state workers, manage private insurance coverage, and license health professionals. Some states also manage medical insurance for low-income homeowners, in addition to Medicaid. In 2017, public costs represented 45 percent of overall health care spending, or around 8 percent of GDP. Federal spending represented 28 percent of total healthcare spending.
Indicators on How Much Does Universal Health Care Cost You Need To Know

The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Providers is the largest governmental source of health protection funding. Medicare is funded through a combination of basic federal taxes, a mandatory payroll tax that pays for Part A (medical facility insurance coverage), and individual premiums. Medicaid is mainly tax-funded, with federal tax incomes representing two-thirds (63%) of costs, and state and local revenues the remainder.
CHIP is funded through matching grants provided by the federal government to states. The majority of states (30 in 2018) charge premiums under that program. Spending on private health insurance coverage accounted for one-third (34%) of total health expenses in 2018. Personal insurance coverage is the main health coverage for two-thirds of Americans (67%).